INNOVATE EFFECTIVELY WITH LEAN STARTUP
The Lean Startup is a methodological approach introduced by Eric Ries in his book The Lean Startup (2011). It is primarily aimed at entrepreneurs and organizations wishing to innovate quickly while minimizing risks and costs. Inspired by the principles of Toyota's Lean Manufacturing, it applies particularly well to software development thanks to its focus on speed, iterative learning, and meeting real user needs.
The Fundamental Principles of Lean Startup
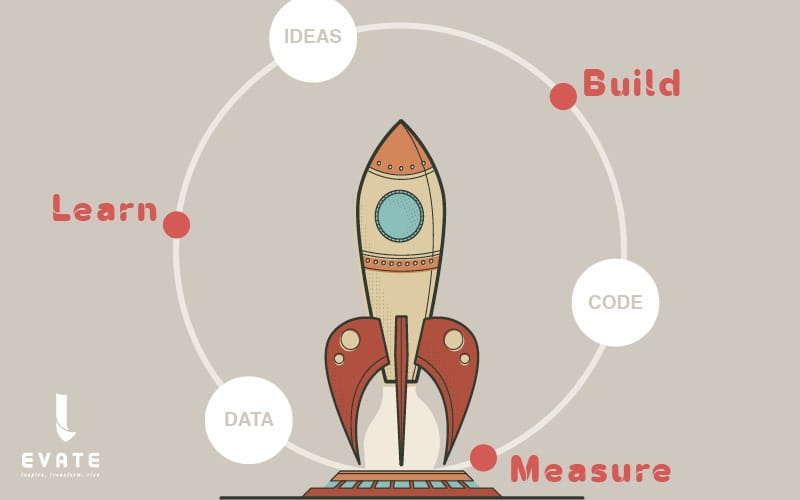
- Build, Measure, Learn The “Build-Measure-Learn” cycle is at the heart of Lean Startup. The idea is to quickly create a minimum viable product (MVP), gather user feedback, and use this data to adjust or pivot.
- Build: Create a simple version of the product or feature to test a hypothesis.
- Measure: Collect quantitative and qualitative data on the use of this product.
- Learn: Draw lessons from this data to refine the product or change direction.
- Minimum Viable Product (MVP) The MVP is a simplified version of the product that allows testing a key hypothesis with minimal effort. The goal is to quickly identify whether an idea has potential before investing heavily in its development. The focus is on core features that provide the most value to the product, enabling the target users to test it.
- Pivot or Persevere Based on the feedback received, a company can either continue with its initial plan (persevere) or pivot, meaning to change its approach or direction to address a more relevant need.
- Validated Learning Unlike assumptions or intuitions, Lean Startup emphasizes learning based on real data. Every decision is made by relying on concrete experiments conducted on the product.
- Concrete Application Examples
- Dropbox: Before developing their product, Dropbox created a simple video explaining the concept of cloud storage. The feedback received allowed them to validate the product's interest before embarking on costly technical development. This was their MVP.
- Airbnb: The founders started by renting out their own apartment in San Francisco and used this experience to test the idea of a housing rental platform. This initial phase validated their concept without needing complex software development.
- Zappos: Before becoming an online shoe-selling giant, Zappos tested the idea by photographing shoes in local stores and selling them online. This rudimentary MVP allowed them to confirm consumer interest in their platform.
Lean Startup in Software Development
In the context of software development, Lean Startup offers a pragmatic approach to creating products that meet user needs and reduce the risks of failure.
- Adaptation to User Needs Traditional software is often developed according to rigid plans, which can lead to a final product that doesn't meet user expectations. With Lean Startup, developers iterate quickly based on user feedback from the earliest stages of the project.
- Cost Reduction By focusing on an MVP, teams avoid developing unnecessary or unwanted features. This allows investment in what really matters.
- Alignment with Agile Methodologies Lean Startup and agile share a common philosophy: rapid iteration, collaboration, and continuous adaptation. For example, a Scrum team can integrate Lean Startup principles by conducting sprints dedicated to creating an MVP or running experiments.
- Continuous Improvement Thanks to validated learning, teams can constantly refine their product. Data collection tools like Google Analytics or solutions like Mixpanel provide clear insights into user behavior.
What Lean Startup Brings to Software Development
- Better Risk Management: By testing key hypotheses early on, Lean Startup limits the chances of creating a product that will not find its market.
- Focus on User Value: Instead of developing unnecessary features, teams focus on real user needs.
- Accelerated Time-to-Market: MVPs enable quick releases of initial versions to beat the competition.
- A Culture of Innovation: Lean Startup encourages teams to experiment, test new ideas, and learn continuously.
Conclusion
Lean Startup is not just a method for startups; it’s a philosophy that applies to large companies and software development teams as well. By promoting rapid learning, iteration, and adaptation, it allows for the creation of products that truly meet user expectations. In an ever-evolving tech sector, this approach provides a valuable competitive advantage by reducing risks while accelerating innovation.
Lean Startup, more than just a method, is a revolution in the way products are conceived and designed.
